from bioMONAI.core import cells3d, img2Tensor
from bioMONAI.visualize import visualize_slicesTransforms
Sampling
Resample
Resample (sampling, **kwargs)
*A subclass of Spacing that handles image resampling based on specified sampling factors or voxel dimensions.
The Resample class inherits from Spacing and provides a flexible way to adjust the spacing (voxel size) of images by specifying either a sampling factor or explicitly providing new voxel dimensions.
Args: sampling (int, optional): Sampling factor for isotropic resampling. Default is 1, indicating no change in resolution. **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments that can include ‘pixdim’ to specify custom voxel dimensions.
Attributes: pixdim (list or tuple): The voxel dimensions of the image after resampling. If not provided during initialization, this will be determined based on the sampling factor and original image properties.*
img = BioImageStack(img2Tensor(cells3d()[:,0]))
visualize_slices(img, showlines=False)
img2 = Resample(4)(img)
visualize_slices(img2, showlines=False)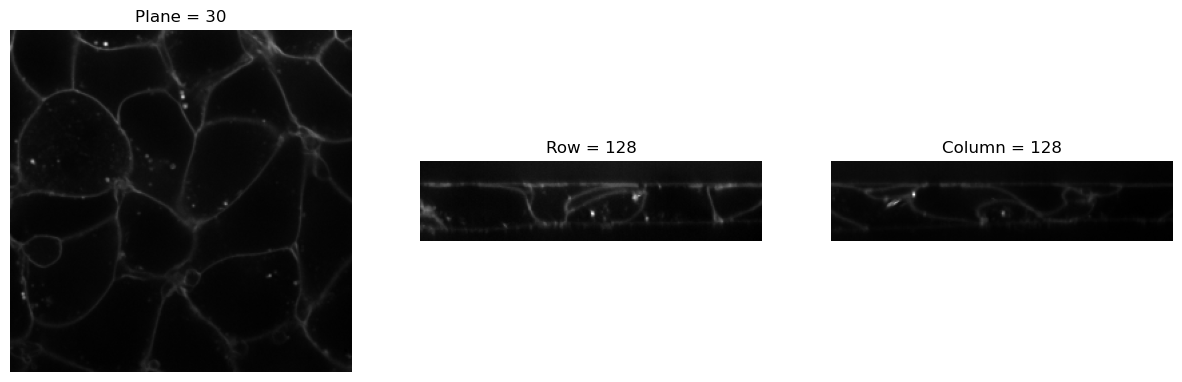

Noise
RandCameraNoise
RandCameraNoise (p:float=1.0, damp=0.01, qe=0.7, gain=2, offset=100, exp_time=0.1, dark_current=0.6, readout=1.5, bitdepth=16, seed=42, simulation=False, camera='cmos', gain_variance=0.1, offset_variance=5)
*Simulates camera noise by adding Poisson shot noise, dark current noise, and optionally CMOS fixed pattern noise.
Returns: numpy.ndarray: The noisy image as a NumPy array with dimensions of input_image.*
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | float | 1.0 | Probability of applying Transform |
| damp | float | 0.01 | Dampening factor to prevent saturation when adding noise |
| qe | float | 0.7 | Quantum efficiency of the camera (0 to 1). |
| gain | int | 2 | Camera gain factor. If an array, it should be broadcastable with input_image shape. |
| offset | int | 100 | Camera offset in ADU. If an array, it should be broadcastable with input_image shape. |
| exp_time | float | 0.1 | Exposure time in seconds. |
| dark_current | float | 0.6 | Dark current per pixel in electrons/second. |
| readout | float | 1.5 | Readout noise standard deviation in electrons. |
| bitdepth | int | 16 | Bit depth of the camera output. |
| seed | int | 42 | Seed for random number generator for reproducibility. |
| simulation | bool | False | If True, assumes input_image is already in units of photons and does not convert from electrons. |
| camera | str | cmos | Specifies the type of camera (‘cmos’ or any other). Used to add CMOS fixed pattern noise if ‘cmos’ is specified. |
| gain_variance | float | 0.1 | Variance for the gain noise in CMOS cameras. Only applicable if camera type is ‘cmos’. |
| offset_variance | int | 5 | Variance for the offset noise in CMOS cameras. Only applicable if camera type is ‘cmos’. |
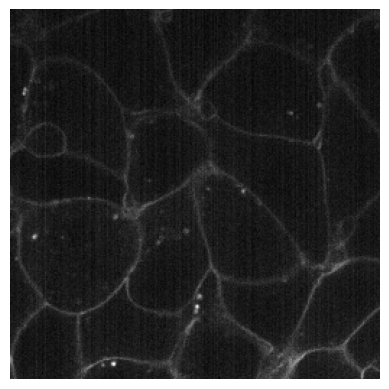
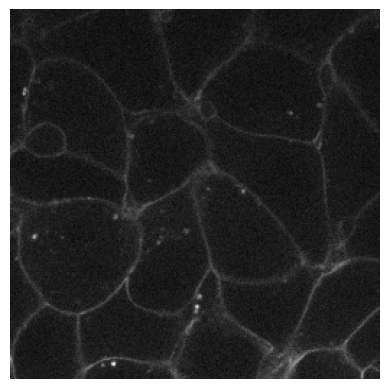
from bioMONAI.visualize import plot_imageimg3 = img[30]plot_image(img3)
plot_image(RandCameraNoise(camera = 'cmos').encodes(img3))
plot_image(RandCameraNoise(camera = 'ccd', readout=2).encodes(img3))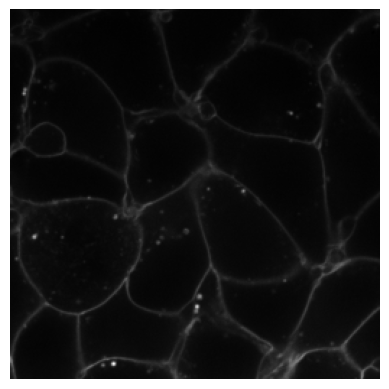
Normalization
ScaleIntensity
ScaleIntensity (x, min=0.0, max=1.0, axis=None, eps=1e-20, dtype=<class 'numpy.float32'>)
Percentile-based image normalization.
ScaleIntensityPercentiles
ScaleIntensityPercentiles (x, pmin=3, pmax=99.8, axis=None, eps=1e-20, dtype=<class 'numpy.float32'>)
Percentile-based image normalization.
ScaleIntensityVariance
ScaleIntensityVariance (ndim=2)
*Scales the intensity variance of an ND image to a target value.
Args: target_variance (float): The desired variance for the scaled intensities. ndim (int): Number of spatial dimensions in the image. Default is 2 for 2D images.*
# Example usage with a random tensor of shape (1, 3, 256, 256)
rand_tensor = BioImageBase(torch.rand(1, 3, 256, 256))
transform = ScaleIntensityVariance(ndim=4)
# Apply the transform to the tensor
scaled_tensor = transform(rand_tensor)
print('Original Tensor Variance:', rand_tensor.var().item())
print('Scaled Tensor Variance:', scaled_tensor.var().item())Original Tensor Variance: 0.08341076225042343
Scaled Tensor Variance: 1.0Data Augmentation
RandCrop2D
RandCrop2D (size:int|tuple, lazy=False, **kwargs)
Randomly crop an image to size
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| size | int | tuple | Size to crop to, duplicated if one value is specified | |
| lazy | bool | False | a flag to indicate whether this transform should execute lazily or not. Defaults to False |
| kwargs |
RandCropND
RandCropND (size:int|tuple, lazy=False, **kwargs)
*Randomly crops an ND image to a specified size.
This transform randomly crops an ND image to a specified size during training and performs a center crop during validation. It supports both 2D and 3D images and videos, assuming the first dimension is the batch dimension.
Args: size (int or tuple): The size to crop the image to. this can have any number of dimensions. If a single value is provided, it will be duplicated for each spatial dimension, up to a maximum of 3 dimensions. **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the parent class.*
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| size | int | tuple | Size to crop to, duplicated if one value is specified | |
| lazy | bool | False | a flag to indicate whether this transform should execute lazily or not. Defaults to False |
| kwargs |
# Define a random tensor
orig_size = (65, 65)
rand_tensor = BioImageBase(torch.rand(8, *orig_size))
for i in range(100):
test_eq((8,64,64),RandCropND((64,64))(rand_tensor).shape)RandFlip
RandFlip (prob=0.1, spatial_axis=None, ndim=2, lazy=False, **kwargs)
Randomly flips an ND image over a specified axis.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| prob | float | 0.1 | Probability of flipping |
| spatial_axis | NoneType | None | Spatial axes along which to flip over. Default is None. The default axis=None will flip over all of the axes of the input array. |
| ndim | int | 2 | If axis is negative it counts from the last to the first axis. If axis is a tuple of ints, flipping is performed on all of the axes specified in the tuple. |
| lazy | bool | False | Flag to indicate whether this transform should execute lazily or not. Defaults to False |
| kwargs |
# Define a random tensor
orig_size = (1,4,4)
rand_tensor = BioImageBase(torch.rand(*orig_size))
print('orig tensor: ', rand_tensor, '\n')
for i in range(3):
print(RandFlip(prob=.75, spatial_axis=None)(rand_tensor))orig tensor: metatensor([[[0.8943, 0.3943, 0.2556, 0.8066],
[0.5016, 0.6177, 0.8749, 0.1229],
[0.9610, 0.1088, 0.5785, 0.6857],
[0.5776, 0.7028, 0.5421, 0.3654]]])
metatensor([[[0.8066, 0.2556, 0.3943, 0.8943],
[0.1229, 0.8749, 0.6177, 0.5016],
[0.6857, 0.5785, 0.1088, 0.9610],
[0.3654, 0.5421, 0.7028, 0.5776]]])
metatensor([[[0.8943, 0.3943, 0.2556, 0.8066],
[0.5016, 0.6177, 0.8749, 0.1229],
[0.9610, 0.1088, 0.5785, 0.6857],
[0.5776, 0.7028, 0.5421, 0.3654]]])
metatensor([[[0.8066, 0.2556, 0.3943, 0.8943],
[0.1229, 0.8749, 0.6177, 0.5016],
[0.6857, 0.5785, 0.1088, 0.9610],
[0.3654, 0.5421, 0.7028, 0.5776]]])RandRot90
RandRot90 (prob=0.1, max_k=3, spatial_axes=(0, 1), ndim=2, lazy=False, **kwargs)
Randomly rotate an ND image by 90 degrees in the plane specified by axes.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| prob | float | 0.1 | Probability of rotating |
| max_k | int | 3 | Max number of times to rotate by 90 degrees |
| spatial_axes | tuple | (0, 1) | Spatial axes along which to rotate. Default: (0, 1), this is the first two axis in spatial dimensions. |
| ndim | int | 2 | |
| lazy | bool | False | Flag to indicate whether this transform should execute lazily or not. Defaults to False |
| kwargs |
# Define a random tensor
orig_size = (1,4,4)
rand_tensor = BioImageBase(torch.rand(*orig_size))
print('orig tensor: ', rand_tensor, '\n')
for i in range(3):
print(RandRot90(prob=.75)(rand_tensor))orig tensor: metatensor([[[0.3961, 0.2351, 0.4363, 0.3366],
[0.9416, 0.8529, 0.8646, 0.0091],
[0.5012, 0.9804, 0.8109, 0.1094],
[0.9639, 0.5107, 0.4666, 0.8632]]])
metatensor([[[0.3961, 0.2351, 0.4363, 0.3366],
[0.9416, 0.8529, 0.8646, 0.0091],
[0.5012, 0.9804, 0.8109, 0.1094],
[0.9639, 0.5107, 0.4666, 0.8632]]])
metatensor([[[0.9639, 0.5012, 0.9416, 0.3961],
[0.5107, 0.9804, 0.8529, 0.2351],
[0.4666, 0.8109, 0.8646, 0.4363],
[0.8632, 0.1094, 0.0091, 0.3366]]])
metatensor([[[0.8632, 0.4666, 0.5107, 0.9639],
[0.1094, 0.8109, 0.9804, 0.5012],
[0.0091, 0.8646, 0.8529, 0.9416],
[0.3366, 0.4363, 0.2351, 0.3961]]])